Obesity is a growing public health problem in the United States as well as in other parts of the world. Overweight patients are more and more turning to bariatric surgery to help them lose the extra pounds and trim their waistline. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more than 37.5% of American adults are obese and 16% of children and teens are considered obese. With obesity costs rising, medical costs now amount to nearly $147 billion each year. Type II Diabetes, heart disease, and stroke are all some of the leading causes of preventable death in the United States and directly connected to obesity.
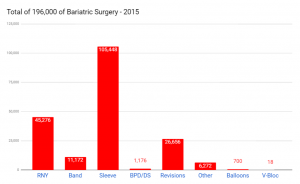 According to ASMBS data, in 2015 nearly 200,000 people underwent bariatric surgery to fight obesity – 53.8% gastric sleeve, 23.1% gastric bypass, 5.7% band, and 13.6% revision surgeries. The total number of surgeries are up 25% from 160,000 in 2011. The data also shows the prevalence of gastric sleeve over other procedures.
According to ASMBS data, in 2015 nearly 200,000 people underwent bariatric surgery to fight obesity – 53.8% gastric sleeve, 23.1% gastric bypass, 5.7% band, and 13.6% revision surgeries. The total number of surgeries are up 25% from 160,000 in 2011. The data also shows the prevalence of gastric sleeve over other procedures.
The bariatric procedures have improved and evolved over the last decade or so. Understanding obesity and its associated destructive effects on overall health help create awareness to proactively concur with this epidemic. Dr. Jacqueline Osuna, a board-certified bariatric surgeon at Mexico Bariatric Center (MBC), discusses the latest in bariatric surgery.
Evolution of the Bariatric Surgery in the Last Decade
The metabolic and bariatric surgery field has evolved tremendously over the past 10 years. Scientific and clinical research, along with advancements in medical technology and minimally invasive surgical techniques, have made the weight loss surgery not only a safer option but one that is much more effective and results in long-term success. The field of bariatrics continues to grow internationally and surgeons now have the ability to complete specialized training and credentialing process, such as board certification in bariatric surgery.
The Most Popular Bariatric Surgeries Now Performed
 Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (LSG) and Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) are prominent weight-loss surgeries performed. These two surgeries account for more than 90% of all bariatric surgical procedures.
Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (LSG) and Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) are prominent weight-loss surgeries performed. These two surgeries account for more than 90% of all bariatric surgical procedures.
- Laparoscopic Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy (LVSG), has been around for 14 years, now is number 1 bariatric surgery. In this procedure the capacity of the stomach is altered by actually removing around 80% of it; the rest of the anatomy is left uncastrated. As a result, the levels of hunger hormone (Ghrelin) is reduced causing a neurohormonal change – changes in the relationship between brain and guts, and consequently patient and food.
- The Laparoscopic Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass (LRYGB), has been performed for more than 40 years, now is in 2nd place. This procedure is a gold standard; a well-studied, researched and reliable procedure. Patients lose weight and get healthier by reducing the capacity of the stomach in addition to rerouting their digestive tract. Rearranging the intestinal tract improves patient’s metabolisms by interfering with different mechanisms of how food gets digested and absorbed.
- A more invasive and less used procedure is Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS), where part of the stomach is removed as it is done in the sleeve and the remaining portion is rerouted to the lower part of the small intestine.
- Once widely used Gastric Banding, or Lap Band, now is outdated and seldom used. The band, placed on the upper part of the stomach, creates a small pouch to limit the amount of food. Once perceived as a reversible procedure, the gastric band has short-term and long-term complications with hardly any weight loss success.
Has Bariatric Surgery Become More Affordable?
The majority of insurance companies, including Medicare and Medicaid, are provided coverage for weight loss surgery to:
- patients with a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 35+ (Kg/m2) and who suffer from obesity-related diseases, such as type II diabetes, hypertension, diabetes, sleep apnea, liver disease, and more
- patient with a BMI of 40+ (Kg/m2)
Unfortunately, the decreasing overall cost of surgery has not made access to morbidly obese patients to this great tool for treatment easier. Bariatric Medical Tourism with quality and affordable pre-packaged procedures is a viable option for uninsured and under-insured patients. Procedures such as gastric sleeve and bypass are available in the range of 4,000 to 6,000, which is a fraction of the cost in the U.S.
Who Qualifies for Bariatric Surgery?
Candidates for this type of surgery typically have some type of metabolic or hormonal factors that contribute to their obesity. Ultimately, weight loss surgery can help them with those issues. It is a tool to help patients get to a normal level. Patients must adopt a new lifestyle in order to be successful with their extreme weight loss. A good surgeon will couple nutrition education and counseling with the support tools used with weight loss surgery patients.
Good candidates for weight loss surgery have a body mass index (BMI) that classifies them as obese. They also may have obesity-related medical conditions or illnesses such as high blood pressure, sleep apnea or diabetes. The patient’s emotional health may also be evaluated prior to approving their request for surgery.
Potential candidates also meet with a dietitian or nutritionist both before and after the surgery in order to create a plan for making lifestyle changes. Follow-up is important after surgery and patients are expected to meet with staff regularly after their surgical procedure.
What are the risks and potential complications of bariatric surgery?
Bariatric surgery has become safer with extremely low mortality rates comparable to commonly performed operations such as gallbladder removal, appendectomy, and hip replacement. The possible complications including:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Exceedingly uncommon, leakage
How Do People Prepare For Bariatric Surgery?
It should be remembered that bariatric surgery, in the end, it is just a great tool that must be used wisely and decisively by the patient to obtain desired results. Pre-op preparation for this life-changing event is of utmost importance. It is crucial to gain more knowledge about nutrition, getting mentally prepared, committing to adopting new and better habits, and to increase physical activity.
Protocols Patients Have To Follow After Surgery For Long-term Success
The long-term success rate following weight loss surgery is more than 85%. Success relies on acquiring a better understanding of the impact that nutrition has on our overall health and being mentally ready to adopt new lifestyle changes. Patients need to adhere to post-op guidelines and key principles that are necessary to achieve adequate and sustainable weight loss. The postoperative diet for a few weeks allows stomach healing:
- Monitoring protein intake to secure adequate nutrition
- Proper hydration
- Compliance with vitamin intake
- Increase of physical activity
- Among other lifestyle and behavioral changes
Benefits of Surgery
A recent study by Stanford University researchers shows that weight loss surgery can even help reverse some signs of aging. Their small study was presented at Obesity Week in November 2013 and focused on telomeres in patients who had bariatric surgery. The caps at the ends of chromosomes that prevent degradation of DNA lengthened dramatically for at least a year after surgery in more than half of these 51 patients. The team and its researchers believe that this study while small shows hope for the first time that bariatric surgery can help reverse some negative effects of obesity and the related diseases patients may have because of it.
